
Class 5 Readings in “Design Kit_The Course for Human-Centered Design.” Dropbox. Web. 14 Mar. 2016.

Key Terms:
- Rapid prototype:
- tests pieces of solution
- low fidelity
- not market ready
- Live prototype:
- tests how well solution resonates with the market
- moderate fidelity
- tests multiple parts of solution
- appears to be market ready
- Pilot:
- version of solution that is holistically feasible and viable in the market place
- high fidelity
- tests whole idea and whole systems
- actually market ready
- Bootstrapping
- no outside partners for funding
- for very lucrative ideas
- PROS: lots of control, can change quickly, not reliant on partner preferences
- CONS: costly, high risk, large staff, slow growth, compete with companies who could be collaborating partners
- Franchising
- selling or licensing product to funding partners
- good when other entrepreneurs like your idea
- PROS: moderate control, less costly, connections to supply chain
- CONS: difficult to maintain quality control, relies on will and preferences of outside partners
- Integration
- combine forces with external organizations
- good when solution complements an existing service or product or when partnering organization has the resources to scale up solution faster
- PROS: high impact, cheap, connected to supply chains, quick scale up
- CONS: difficult to maintain quality control, loss of control, reliant on will and preferences of partners
STEPS in IMPLEMENTATION PHASE:
- Understand your target:
- what does solution mean to clients and those involved in its implementation?
- what’s the capacity of the implementation group?
- plot solutions in an Innovation 2×2 chart to identify incremental, evolutionary, and revolutionary ideas
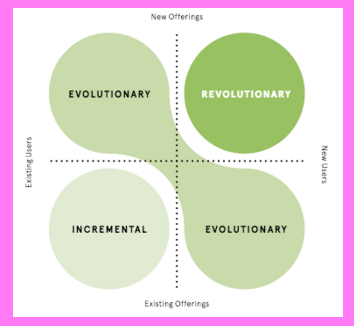
- clarify user group (new or existing) for each solution
- identify and test solutions that fit gaps in the Innovation 2×2 chart
- Create an action plan:
- plan how design will make it to the market – identify key processes and partners
- make a roadmap – calendar that shows key milestones and interactions with key stakeholders
- staff project – assemble a team with specific skills or access to funding needed to implement products
- build partnerships – identify key partners and build relationships with these
- develop funding short-term and long-term funding strategies – short-term strategy is for product launch until sufficient penetration to market that it can get access to sustainable sources of revenue
- create a pitch
- explain how product works, why it counts, who benefits
- modify pitch for different listeners
- Launch your Solution:
- test idea in the real market place
- run a life prototype, stress test for market conditions
- define what to test. testable items include:
- pricing – how will it vary? how does it compare to competitor products?
- payment options – upfront? installments? subscriptions?
- incentives – how to pay employees? commissions?
- customer retention – which customers are most important? how to retain these?
- customer experience – are customers interested in product? does interest linger?
- go to pilot
- test ideas AND systems
- done after testing and refining a few live prototypes
- idea has proven to be feasible, desirable, viable, and scalable
- Keep getting Feedback & Iterating:
- keep getting feedback:
- measure and evaluate work
- dedicate a team to gathering feedback
- include key stakeholders:
- convene many stakeholders to get lots of feedback
- document feedback
- keep iterating
- improve solutions using feedback
- tweak things such as:
- communications strategy
- distribution plans
- keep getting feedback:
- Scale Towards Impact
- define success
- determine what success looks like over different time periods
- sustainable revisions
- assess new strategies
- total costs?
- reliability of funding?
- what relationships needs to be built?
- how much to sell to stay viable?
- how to retain customers?
- launch new products over time?
- scaling options – add locations? add products?
- assess new strategies
- measure & evaluate:
- identify measured of success and how to measure them
- define success

Practicing the Implementation phase teaches students and teachers how to implement REAL solutions that impact people outside school. This phase can be used to scaffold the most authentic projects in which students design solutions that will be actually used by (and perhaps sold to) people outside school.

Preparation Steps
- HCD Implementation Steps applied to Solving Student Learning Design Challenge
- Recruit an implementation team (small) who has the skills needed to help you test and implement your live solutions
- Decide which of the implementation steps above are practical to trial in a school setting
- Decide which solutions you will take through live trials
- Scaffolding HCD Implementation Steps for Students
- Experience HCD process prior to facilitating it to learn how to better scaffold it
- Let students in design teams select a worthy design challenge (or assign one)
- Guide them through a student friendly, time affective version of the Inspiration phase
- Guide them through a student friendly, time affective version of the Ideation: synthesis phase
- Guide them through a student friendly, time effective version of the Ideation:prototyping phase
- Develop visuals and assign readings that teach students how to go through key steps in a student friendly, time effective version of the Implementation phase.
- Build relationships with community partners who can assist students with testing and implementing their solutions in authentic settings
Early Implementation Steps
- HCD Implementation Steps applied to solve student learning design challenge
- Plot solutions in Innovation 2×2 chart. See above
- Use Innovation 2×2 analysis to get inspiration for new solutions to iteration if needed
- Create an action plan. See above.
- Launch solution. see above.
- Gather feedback and continue to iterate. See above.
- Determine impact scale of solution and take steps to bring it to that scale. See above.
- Scaffolding HCD Implementation Steps for Students
- Facilitate student design teams through a student friendly, time-effective version of the steps listed above
Advanced Implementation Steps
- HCD Implementation Steps applied to solving a student learning design challenge
- Reflect on the entire HCD process
- Decide which steps in the process would be appropriate for scaffolding projects of varying levels of authenticity. Start to implement these phases and related scaffolds into student projects.
- Scaffolding HCD Implementation Steps for Students
- Let students reflect on how Implementation Steps can be used to implement and test solutions in other courses and in their own lives
- Have students reflect on how the HCD process changed their view of themselves as learners and as potential entrepreneurs
- Build relationships with actual companies who would like to implement real student solutions so that all HCD Phases can be implemented to a high degree of fidelity. For 2 tools to building relationships with partner, see this article.
