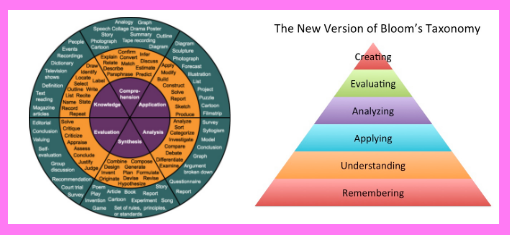
- Knowledge
- recall, remember
- Trigger words: tell, recite, list, remember, memorize, define
- Products: worksheets, quizzes, tests, skills work, vocabulary work, facts in isolation
- Comprehension
- restate concepts in own words
- Trigger words: restate in own words, give examples, explain, summarize, translate, summarize, translate
- Products: drawings, diagrams, responses to questions, revisions, translations
- Application
- transfer knowledge from one context to the next
- Trigger words: demonstrate, use guides, maps, charts, etc., build, cook
- Products: recipe, model, artwork, demonstration, craft
- Analysis
- understand how parts relate to a whole
- trouble shoot
- understand structure and motive
- Trigger words: investigate, classify, categorize, compare, contrast, solve
- Products: survey, questionnaire, plan, solution to problem report, prospects
- Evaluation
- judge value of something using criteria
- support judgement
- Trigger words: judge, evaluate, give opinion, give viewpoint, prioritize, recommend, critique
- Products: decision, rating/grades, editorial, debate, critique, defense, verdict, judgement
- Synthesis
- reform individual parts to make a new whole
- Trigger words: compose, design, invent, create, hypothesize, construct, forecast, rearrange, imagine
- Products: lesson plan, song, poem, story, advertisement, invention, other creative products

The Bloom’s taxonomy levels can be used to create questions and activities at different levels of thinking. The varied products can be used develop menus of products that match the same learning targets to differentiate instruction. The top 3 levels can serve as extension activities for gifted students.

Preparation Steps
- Analyze standards and write aligned long term and supporting learning targets
- Determine which cognitive levels match a range of thinking that is appropriate to the learning targets
- Use range of cognitive levels to design different options for scaffolding learning targets that can be used to differentiate instruction and offer student choice
- Use trigger words to design good questions sequences that explore range of cognitive levels for each learning target
Early Implementation Steps
- Initiate discussions that involve ALL students using questions sequences designed by using learning targets and thinking trigger words. See this article for ideas on how to increase student participation.
Advanced Implementation Steps
- Teach students Thinking Levels and associated trigger words and products. Use this as a tool for students to ask better questions and to create alternative product choices for project.
- Incorporate thinking level activities and learning targets into scaffolding that uses differentiated curriculum charts to offer students choices on how to learn and demonstrate mastery of learning targets

- Differentiated Instruction articles
- Questioning Strategies articles
- Understanding articles