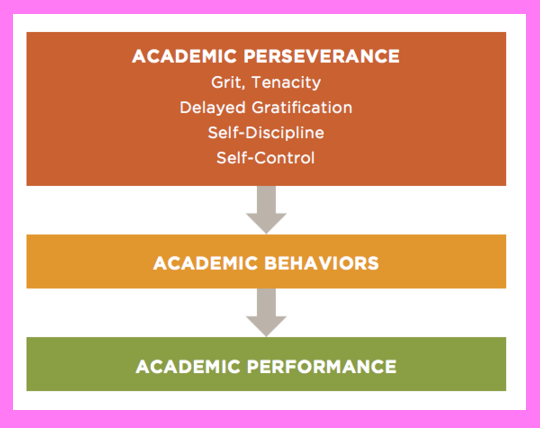
Academic perseverance:
- related to student effort and quality of academic behavior
- initial and sustained momentum
- helpful for short-term and long-term achievement
- can be impacted by academic mindsets, academic skills, learning strategies, personality
- grit: sticking to long-term goals despite obstacles
- self-control: foregoing short-term temptations to prioritize higher goals
Grit & self control
- 10 years of sustained practice to become an expert
- grit involves working steadfastly on one goal over sustained period of time
- Grit Scale – measures 2 dimensions of grit – consistency of interests & persistence of effort
- self control – ability to avoid impulsive behavior and fulfill short-term obligations (e.g. reading test instructions before starting questions)
Relationship between academic perseverance and academic performance:
- evidence that grit can make up for lack in tested achievement in standardized tests
- measures of self control correlate to grades
Is academic perseverance malleable?
- it’s harder to change overall grit which research shows to be a more fixed characteristic of people’s characteristics
- more specific academic perseverance is responsive to context
Role of classroom context in shaping academic perseverance:
- classroom contexts that support students’ success at tasks and provide students with strategies to make tasks easier tend to encourage academic perseverance
- contexts that discourage success can decrease academic perseverance
- strategies tied perseverance – time management, managing study environment, rehearsal, effort regulation
- contexts can shape academic mindsets which affect perseverance
Actionable strategies for increasing strategies:
- Direct strategies:
- teaching behaviors associated with impulse control and persistence
- not a lot of research on long term effects of these methods
- Indirect strategies:
- supporting academic mindsets
- helping students feel greater sense of belonging, engagement and confidence can enhance persistence
- teaching learning strategies
- correlated to completed homework completion
- supporting academic mindsets
Summary of research:
- little known on how to make people grittier in many contexts
- promoting positive academic mindsets can build specific academic persistence
- teaching learning strategies can help students complete hard tasks

Enhancing students’ academic perseverance can increase both the quantity and quality of their academic work. Knowing how to create contexts and teach strategies that increase student academic persistence can help them succeed better and more at challenging academic tasks.

Preparation Steps
- Research mindsets and skills that relate to academic persistence
- Create character learning targets that describe sills related to academic persistence
- Research and design learning activities that help students achieve character learning targets related to academic persistence
- Use Grit Scale to pre-assess students’ persistence levels
Early Implementation Steps
- implement activities that promote mindsets and teach academic skills related to academic persistence
- Have students reflect on how they are progressing towards character learning targets related to academic persistence
- Use multiple measures of Grit Scale to see scaffolding related to academic persistence is having any effects on students’ grit levels
Advanced Implementation Steps
- Have students identify the factors strategies that are having the most positive impacts on their grit levels and incorporates these into classroom systems and routines

- Agency articles
- Learning targets